Smart Contract Architecture – STBL
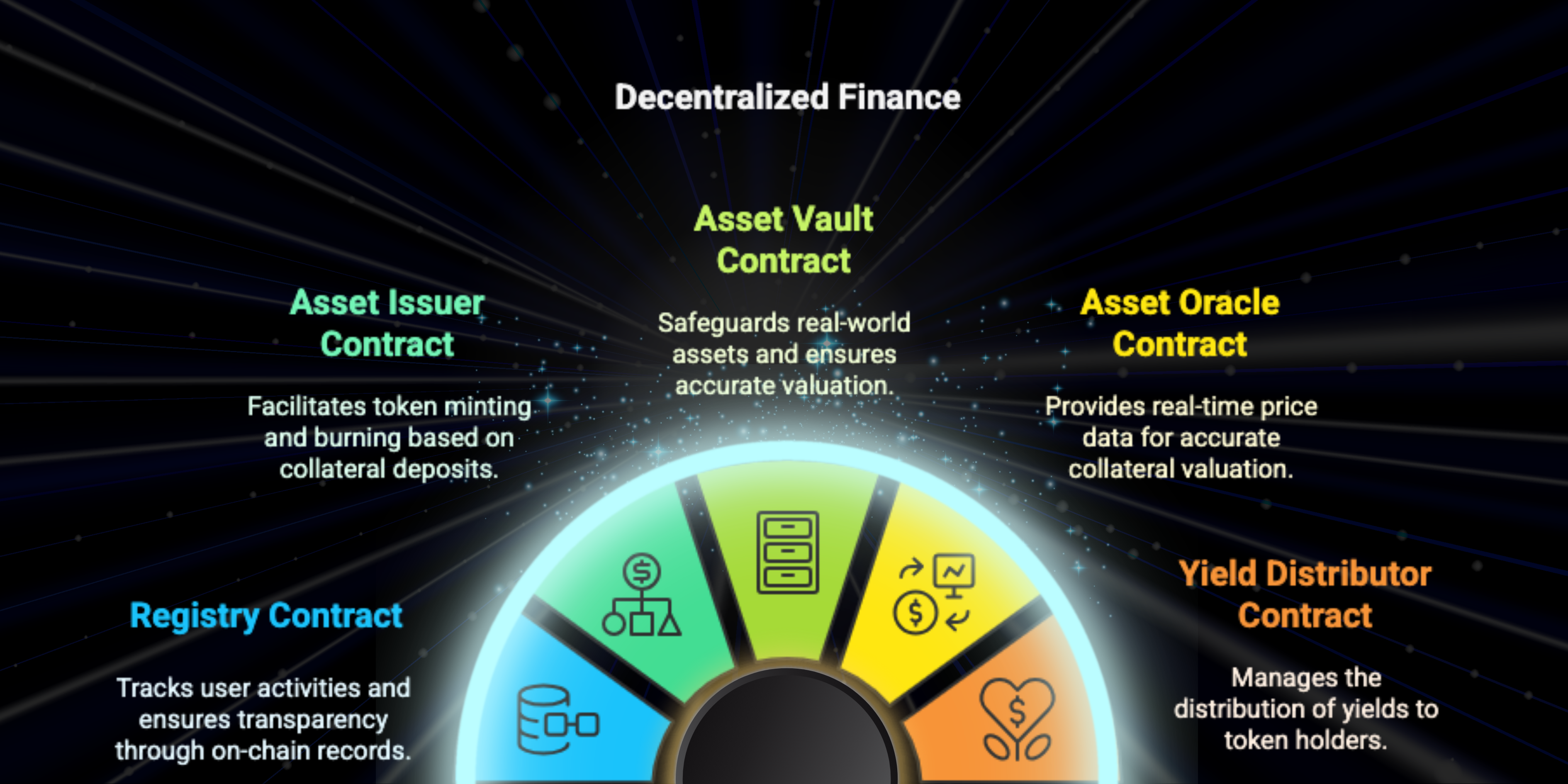
The Smart Contract Architecture of STBL is meticulously designed to ensure security, transparency, and seamless automation of its core functions. By leveraging blockchain technology, STBL decentralizes its operations, providing trustless management of collateral, token issuance, and yield distribution.
1. Overview of Smart Contracts
STBL utilizes multiple interconnected smart contracts to manage the lifecycle of its stablecoin (USST), yield token (YLD), and collateralized assets. The primary contracts include:
- Registry Contract: Maintains records of all user activities, deposits, withdrawals, and token mints or burns.
- Asset Issuer Contract: Facilitates the minting of USST and YLD tokens based on deposited collateral.
- Asset Vault Contract: Securely holds tokenized real-world assets (RWAs) like U.S. Treasury Bills.
- Asset Oracle Contract: Fetches real-time price data from external oracles to ensure accurate asset valuations.
- Yield Distributor Contract: Manages the distribution of yields generated from the Treasury’s investments.
- Governance Contract: Allows YLD token holders to propose and vote on protocol upgrades and parameter changes.
2. Key Components and Functions
a. Registry Contract
- Tracks all essential protocol data, including user balances, collateral deposits, and token issuance.
- Ensures transparency by maintaining a permanent on-chain record of transactions.
- Facilitates efficient query and audit capabilities.
b. Asset Issuer Contract
- Mints new USST and YLD tokens based on the user’s deposited collateral.
- Ensures that all token issuance adheres to the protocol’s over-collateralization requirements.
- Facilitates the burning of tokens during redemptions or liquidations.
c. Asset Vault Contract
- Safeguards all deposited RWAs and tracks their real-time value.
- Works in coordination with the Asset Oracle Contract to ensure accurate valuation of assets.
- Provides instant liquidity by converting RWAs into stablecoin reserves when necessary.
d. Asset Oracle Contract
- Integrates with multiple trusted oracle services for real-time price data.
- Provides accurate collateral valuation, ensuring proper risk management.
- Triggers liquidation events when collateral values fall below the required threshold.
e. Yield Distributor Contract
- Allocates yield generated from the Treasury’s investments to YLD token holders.
- Tracks user balances to ensure accurate and fair distribution of rewards.
- Supports yield reinvestment options to maximize returns.
f. Governance Contract
- Empowers YLD token holders with voting rights to participate in decision-making.
- Allows users to propose and vote on changes in the protocol’s parameters.
- Facilitates decentralized upgrades and ensures community-driven growth.
3. Process Flow of Smart Contracts
-
Collateral Deposit:
- Users deposit tokenized RWAs through the Deposit Contract.
- The deposit details are recorded in the Registry Contract.
- The Asset Vault Contract secures the deposited assets.
-
Token Issuance:
- Based on the deposited collateral, the Asset Issuer Contract mints USST and YLD tokens.
- Over-collateralization is enforced to maintain price stability.
-
Price Verification:
- The Asset Oracle Contract constantly monitors the price of RWAs.
- In case of market volatility, it ensures the collateral remains sufficient.
-
Yield Generation and Distribution:
- The Treasury generates yield from RWAs.
- The Yield Distributor Contract calculates and distributes rewards to YLD token holders.
-
Token Burn and Redemption:
- Users can redeem USST for equivalent collateral through the Asset Issuer Contract.
- Tokens are burned to maintain the $1 peg for USST.
-
Governance Actions:
- Users propose and vote on protocol changes through the Governance Contract.
- Successful proposals are implemented via smart contract upgrades.
4. Security and Auditing
- Automated Audits: Regular on-chain audits ensure transparency and prevent malicious activities.
- Immutable Contracts: Smart contracts are deployed on the blockchain, making them tamper-proof.
- Oracles with Redundancy: Multiple data sources prevent manipulation through oracle attacks.
- Fail-Safe Mechanisms: Emergency shutdown functions safeguard user funds in case of anomalies.
The Smart Contract Architecture of STBL serves as the backbone of its decentralized financial ecosystem. By automating token issuance, collateral management, and yield distribution, STBL ensures transparency, security, and stability. Through its governance mechanisms, the protocol remains adaptable to community-driven improvements, fostering long-term growth and sustainability.